Love for piano remains many decades later
Tuesday, March 3, 2020 by Mary O'Connor | pianists
At 90 years of age, she has recently cut back a bit on her musical engagements, but she is still the official pianist for Club 55+ and happily plays hymns and old favourites for residents in her seniors’ complex in New Glasgow.
“My parents were both great singers and we had a piano at home, so I was anxious to play. I was sent for eight lessons and that is the full extent of my musical education.”
She was nine or ten when she travelled by horse and sleigh from Iron Ore to Stellarton with an uncle who brought butter, eggs and vegetables to town to sell on Saturday mornings.
“He dropped me at Langston Miller’s on Rundle Street and that’s where I learned all the notes. After that, it was just practice. I still play a lot by ear.”
Read the entire article at Love for piano remains many decades later - Community - The News.
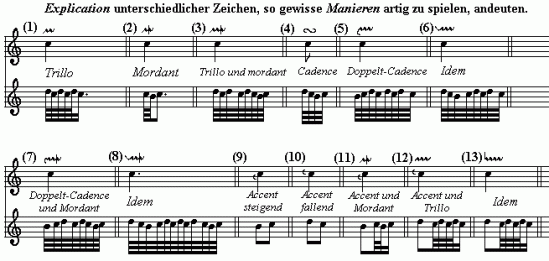
Ornaments, Not Just For Christmas
Monday, August 12, 2019 by Mary O'Connor | pianists
The following ornament table is a transcription of the one appearing in the Clavier-Büchlein vor Wilhelm Friedemann Bach, written by Johann Sebastian Bach for the keyboard instruction of his eldest son.
A scan of the original manuscript appears at Dave's J.S. Bach Page.
The German title translates as "Explanation of various signs, showing how to play certain ornaments correctly."{1} Bach gives the sign for each ornament on the upper of the paired staves, while the lower shows its execution directly beneath.
(This blog has) simply modernized the clefs in my transcription, since Bach's manuscript uses soprano clefs, as several composers continued to do throughout the 18th century in place of the treble clef now used in all keyboard music.
After the transcription graphic showing the table, there appear clickable buttons which are keyed to AU sound files; you can click on any of the ornaments and hear a sound file play its execution.
Read the original blog post with the ornament table and listening files at J.S. Bach's Ornament Table.
Van Cliburn, American Classical Pianist
Wednesday, February 27, 2019 by Mary O'Connor | pianists
Van Cliburn was just a pianist much the way Neil Armstrong was merely an astronaut. Simply put, the tall Texan's musical talent and successes were out of this world.
Cliburn, who died Wednesday February 27, 2013 at age 78 at his Fort Worth home due to complications from bone cancer, was 23 when he strode into Moscow for the inaugural International Tchaikovsky Competition, created to showcase Soviet cultural superiority.
Playing with unerring precision and sublime emotion, he took the top prize and was given a ticker-tape parade in Manhattan, the first and last time a pianist won such an honor.
"Imagine galvanizing the attention of the entire world in the pre-Internet, pre-global TV year of 1958," says Howard Reich, who got to know the Texas-based pianist while researching his 1993 biography, Van Cliburn. "As a Texan, he was so emblematic of the United States. But the Russians fell in love with his romanticism."
In many ways, however, that seminal performance both made his name and sealed his fate.
The pieces that won him the competition — Tchaikovsky's Piano Concerto No. 1 and Rachmaninoff's Piano Concerto No. 3 — sold countless records (his Tchaikovsky No. 1 was the first classical record to sell more than a million copies) and became required concert staples.
"Playing on that treadmill for the next 20 years led him to burn out, and by 1978 he looked terrible and bowed out of public life," says Reich. "He was a gentle soul, and that harsh public spotlight had a negative effect on him."
It would be nine years before Cliburn performed again, at the White House for Ronald Reagan and Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev. Although he made occasional appearances in the following decades, he spent most of his time overseeing his foundation and a quadrennial competition that bears his name.
"I can't think of anyone who has done more to help promote the instrument and young performers than Van," says Cliburn's friend Yoheved Kaplinsky, chairman of the piano department at New York's Juilliard School of Music, which Cliburn attended. "He was an icon in Fort Worth, and a person of great humility."
Born Harvey Lavan Cliburn Jr. in Shreveport, La., Cliburn started piano lessons at age 3 and immediately showed prowess under the watchful eye of his mother, who had trained on the instrument under a teacher who had studied with Franz Liszt.
After moving to Texas, Cliburn played with Houston's symphony at age 12, and at 17 entered Juilliard. At 20, he performed with the New York Philharmonic at Carnegie Hall, setting the stage for his triumphant coup in Russia.
No one can imagine a ticker-tape parade for a pianist in this era, but in Cliburn's heyday he was as much an inevitable cultural icon as he was a reluctant political figure. In the late '50s, the Cold War was raging, the Beatles were still practicing and classical music still held sway.
But what truly made Cliburn unique was the humble ease with which he went about seducing the alleged enemy.
"Van marched in full of the musical values of the Old World, full of tremendous sincerity and with a remarkable ability to connect with audiences," says Kaplinsky. "He may have transcended the boundaries of the art world and breached into the political world, but foremost Van was a consummate artist."
That artistry is on display in various YouTube clips of Cliburn reprising his competition-winning form in Moscow in 1962. The pianist's eyes are often closed as massive hands fly across the length of the keyboard. Utterly lost in the music, Cliburn seems almost oblivious to his audience.
"He had more of everything," says Reich. "More height, more smiles, more sweep on the piano."
In his later years, Cliburn collected the usual array of awards accorded cultural heroes. A Kennedy Center Honors tribute in 2001, a Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2003, and in 2004 Russia's equivalent, the Russian Order of Friendship. In 2004, there was a predictable Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award, and in 1994 a less-expected guest appearance as himself in the TV cartoon Iron Man.
On the personal front, Cliburn was a devout Baptist but also quietly gay; in the late '90s, his longtime partner, Thomas Zaremba, unsuccessfully sued the pianist over compensation claims.
Ultimately, Cliburn will be remembered not just as a performer of startling skill, but also as a global cultural sensation in the age of shortwave radio.
"He did something that no one could have ever imagined back then," says Reich. "He was ubiquitous."
Adapted from USA Today
Related articles
- Van Cliburn, American classical pianist, dies (mercurynews.com)
- Pianist Van Cliburn dies aged 78 (bbc.co.uk)
- Legendary pianist Van Cliburn dies at 78 (star-telegram.com)
- Classical Pianist Van Cliburn Dies (voanews.com)
- Cold War Uniting Pianist Van Cliburn Dies, Aged 78 (contactmusic.com)